Computing systems developer Nvidia is introducing a new cloud-based system for testing autonomous vehicles using photorealistic simulation, with the aim of creating a safer, more scalable method for bringing self-driving cars to the world’s roads.
Nvidia’s founder and CEO, Jensen Huang, has announced that Drive Constellation, a computing platform based on two different servers, will be available to early access partners in the third quarter of 2018.
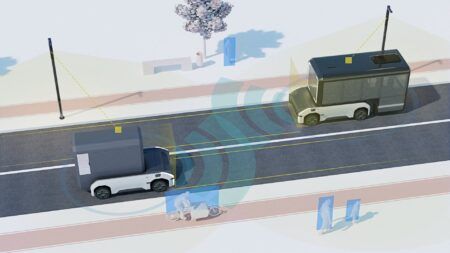
The first server runs the company’s Drive Sim software to simulate a self-driving vehicle’s sensors, such as cameras, lidar and radar. The second contains a powerful Drive Pegasus AI (artificial intelligence) car computer that runs the complete autonomous vehicle software stack and processes the simulated data as if it were coming from the sensors of a real car driving on the road.
The simulation server is powered by Nvidia GPUs (graphics processing units), each generating a stream of simulated sensor data, which feed into the Drive Pegasus for processing. Driving commands from Drive Pegasus are then fed back to the simulator, completing the digital feedback loop. This hardware-in-the-loop cycle, which occurs 30 times a second, is used to validate that algorithms and software running on Pegasus are operating the simulated vehicle correctly.
Drive Sim software generates photoreal data streams to create a vast range of different testing environments. It can simulate different weather such as rainstorms and snowstorms, blinding glare at different times of the day or limited vision at night, and all different types of road surfaces and terrain. Dangerous situations can be scripted in simulation to test the autonomous car’s ability to react, without ever putting anyone in harm’s way.
“Deploying production self-driving cars requires a solution for testing and validating on billions of driving miles to achieve the safety and reliability needed for customers,” explained Rob Csongor, vice president and general manager of automotive systems at Nvidia.
“With Drive Constellation, we’ve accomplished that by combining our expertise in visual computing and datacenters. With virtual simulation, we can increase the robustness of our algorithms by testing on billions of miles of custom scenarios and rare corner cases, all in a fraction of the time and cost it would take to do so on physical roads.”
Luca De Ambroggi, research and analyst director at IHS Markit, commented, “Autonomous vehicles need to be developed with a system that covers training to testing to driving. Nvidia’s end-to-end platform is the right approach. Drive Constellation for virtually testing and validating will bring us a step closer to the production of self-driving cars.”